
簡介
QuirkyLoader 是最近觀察到的一種 Loader,自 2024 年底以來一直活躍地傳遞各種知名的 malicious payload,包括 Agent Tesla、AsyncRAT、FormBook、MassLogger、Remcos、Rhadamanthys 和 Snake Keylogger [1]。本報告著重於此 Loader 的設計和行為的技術層面:多階段感染鏈、透過 Native AOT 編譯的 .NET-based loader module、在注入前的加密解密 routine,以及用於 staging execution 的 Process hollowing 序列。我們的目標是提取可用的工程見解,以實現獨立於表面指標或特定 payload 家族的偵測和預防策略。

感染鏈
感染序列始於透過電子郵件傳遞的壓縮檔案,其中包含三個主要 Artifact:一個合法的可執行檔、一個加密的 payload 和一個作為 loader module 的 .NET DLL。執行這個良性可執行檔會觸發 DLL side-loading,將這個惡意的 Loader 帶入記憶體。然後,該 Loader 會從磁碟上定位並讀取加密的 payload,在記憶體中對其進行解密,並將產生的二進位檔注入到一個獨立的 process 中進行 execution [1]。
下圖從高層次總結了感染鏈;隨後的部分將進行以程式碼為中心的分析。
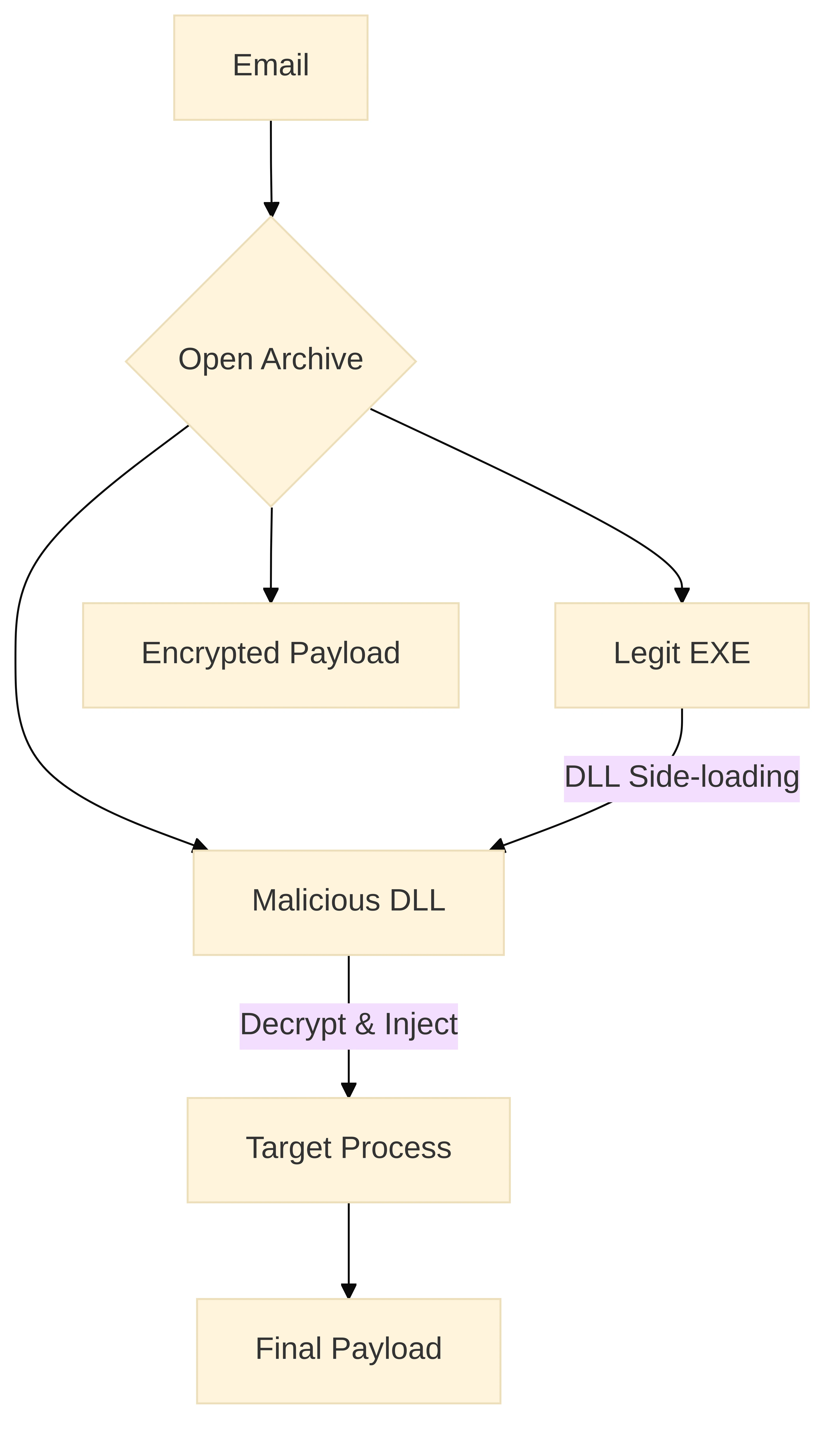
Loader Module (.NET with Native AOT)
這個 loader module 是以 C# 編寫的,並使用 Native Ahead-of-Time (AOT) 編譯發佈。透過 Native AOT 發佈會發出一個 self-contained 的 native image,並移除對 resident CLR/JIT 的 run-time 依賴。這改變了靜態和動態的可觀察性:managed assembly 典型的 PE metadata 會被最小化,run-time reflection 和 dynamic loading 會受到限制,並且啟動延遲可以降低。這些屬性符合 Loader 的操作要求,並有助於規避針對 managed-run-time 啟發式 tuned 的 control [1][4]。
Native AOT,正如官方文件所述,在發佈時將 IL 編譯為機器碼,針對特定的 run-time identifier,並排除 JIT-based code generation。它還鼓勵 trimming of unused code 並對需要 dynamic code paths 的 API 施加限制 (例如,
System.Reflection.Emit
) [4]。在 QuirkyLoader 的 Context 中,這些限制透過 explicit Win32 interop 和 run-time dynamic function resolution 得到緩解,使 execution path 保持確定性和緊湊,同時避免 managed-specific telemetry [1][4]。
加密解密 routine
在注入之前,Loader 會透過
CreateFileW
和
ReadFile
解密從磁碟讀取的一個加密 buffer。一個公開描述的 variant 利用了 CTR 模式下的 Speck‑128,這是一種在 malware 報告中不常見的輕量級 ARX block cipher。在 CTR 模式中,一個 nonce 和擴展的 round keys 驅動 keystream generation;keystream 與 16 位元組的 ciphertext blocks 進行 XOR 運算以還原 payload [1]。實際上,防禦者可以尋找以下簽章:緊接在 interprocess memory writes 之前,出現一連串的 file reads,接著是 over a buffer with a 16‑byte stride 的緊密 ARX loops (rotate-add-xor)。
- __int64 __fastcall SPECK_128_KeyStream(__int64 *Nonce_Lower_Half, __int64 *Nonce_Upper_Half, __int64 Round_Keys) {
- __int64 result; // rax
- __int64 v4; // r10
- LODWORD(result) = 0;
- if ( Round_Keys && *(Round_Keys + 8) >= 32 ) {
- do {
- *Nonce_Lower_Half = *(Round_Keys + 8LL * result + 16) ^ (*Nonce_Upper_Half + __ROL8__(*Nonce_Lower_Half, 56));
- *Nonce_Upper_Half = *Nonce_Lower_Half ^ __ROL8__(*Nonce_Upper_Half, 3);
- result = (result + 1);
- } while ( result < 32 );
- } else {
- do {
- v4 = *Nonce_Upper_Half + __ROL8__(*Nonce_Lower_Half, 56);
- if ( result >= *(Round_Keys + 8) ) ERR_Mb_15();
- *Nonce_Lower_Half = *(Round_Keys + 8LL * result + 16) ^ v4;
- *Nonce_Upper_Half = *Nonce_Lower_Half ^ __ROL8__(*Nonce_Upper_Half, 3);
- result = (result + 1);
- } while ( result < 32 );
- }
- return result;
- }
程式 1. Speck‑128 variant 的 Keystream generation,如公開報告 [1] 所觀察到的。
Process hollowing
Loader 協調了一個 canonical hollowing sequence:它以 suspended 狀態生成一個 target,unmaps the original image,將解密後的 image 寫入遠端 address space,將 thread Context 重新對齊到 payload 的 entry point,然後 resume execution。Hollowing 在公開框架中被明確地 cataloged 為一種 defense-evasion 和 privilege-escalation sub-technique (T1055.012),其特點是特定的 API 用法和排序 [3]。
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "CreateProcessW" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "OpenProcess" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "TerminateProcess" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "CloseHandle" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "GetThreadContext" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "Wow64GetThreadContext" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "SetThreadContext" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "Wow64SetThreadContext" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "ResumeThread" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "VirtualAllocEx" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_ntdll, "ZwUnmapViewOfSection" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_ntdll, "ZwWriteVirtualMemory" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "VirtualProtectEx" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "FlushInstructionCache" )
- GetProcAddress ( base_kernel32, "ReadProcessMemory" )
程式 2. 典型的 hollowing path 動態解析 API set [1][3]。
架構選擇與防禦啟示
透過 Native AOT 發佈 Loader 產生了可預測的、unmanaged execution flow,同時減少了 managed-run-time artifacts。該設計轉向了 explicit API resolution 和 Win32 interop,這使得 early static imports 稀疏,並在 run-time 實現了 conditional behavior。從防禦者的角度來看,有彈性的分析應該綁定到 semantic invariants:由不受信任的父程序所建立的 suspended-process;unmap calls 之後接著是 image-sized remote writes;thread-context pivots 到 non-header entry points;以及銜接 file read 和 remote write 的 tight ARX loops。這些訊號對於 family changes 和 refactoring 來說是強健的 [1][3][4]。
偵測與強化指南
有效的 countermeasure 包括:deny non-interactive execution 的政策 control,針對經常被用作 hollowing hosts 的濫用二進位檔; file-read bursts、ARX loops 和 remote writes 的 telemetry correlation;對將 execution 重新導向到 mapped module headers 之外的 thread-context changes 進行 alerting;以及 strict managed workloads 的 allow-listing,這些 workloads 必須在 CLR 下執行,針對意外 Context 中的 native-only loaders 提高 anomaly scores。在可能的情況下,用 memory operation 和 thread state telemetry 豐富 endpoint,使 hollowing 可以在沒有脆弱簽章的情況下被偵測到 [3][4]。
結論
QuirkyLoader 代表了惡意軟體載入器技術的複雜演進,其特點是其多階段感染鏈、基於 .NET 的 DLL 模組使用原生 AOT 編譯以及先進的 Process hollowing 技術。採用 Speck-128 等不常見的加密演算法進一步凸顯了 Threat actor 規避傳統偵測機制的意圖。本技術分析強調,QuirkyLoader 的設計著重隱蔽性和效率,能夠投遞各種 Malicious Payload,同時最大限度地減少其占用空間並規避安全工具的檢測。
了解這些技術複雜性對於制定強大的防禦策略至關重要。防禦者不應依賴脆弱的簽章,而應專注於行為分析,以識別 QuirkyLoader 操作的不變特徵,例如動態 API 解析、Process hollowing 期間的特定記憶體操作模式以及獨特的加密例程。透過專注於這些基本技術面,組織可以建立更具彈性的偵測和緩解能力,以應對 QuirkyLoader 以及類似不斷發展的威脅。
參考文章
- [IBM X-Force Threat Analysis: QuirkyLoader - A new malware loader delivering infostealers and RATs]
- [QuirkyLoader - The New Malware Loader Spreading Infostealers and Remote Access Trojans]
- [Process Injection: Process Hollowing, Sub-technique T1055.012 - Enterprise | MITRE ATT&CK®]
- [Native AOT deployment overview - .NET | Microsoft Learn]